Index
HeartWare

Challenge:
Aiming to support schoolchildren in learning to write through the possibilities of modern sensors and AI, STABILO has developed an innovative product: the Digipen. Inspired by this product, we asked ourselves whether a digital pen could also serve as an innovative input device for digital games. The goal of this project was to explore whether a DigiPen could provide new, unique gaming experiences compared to traditional input devices such as keyboards, mice, or game controllers. Accordingly, in summer semester 2024 we gave students of the lecture “Designing Gamified Systems” the following challenge:
Develop an innovative game concept (single-player or multiplayer) in which a DigiPen is used as the input device, and that players rate the gaming experience more positively compared to using traditional input devices for games.
Lecture: Designing Gamified Systems
Date: Summer semester 2024
Results:
HeartWare
Team:
Erika Sanchez Wong, Xhovana Prenga, Felix Schuhmann, Mahakdeep Kaur
Abstract:
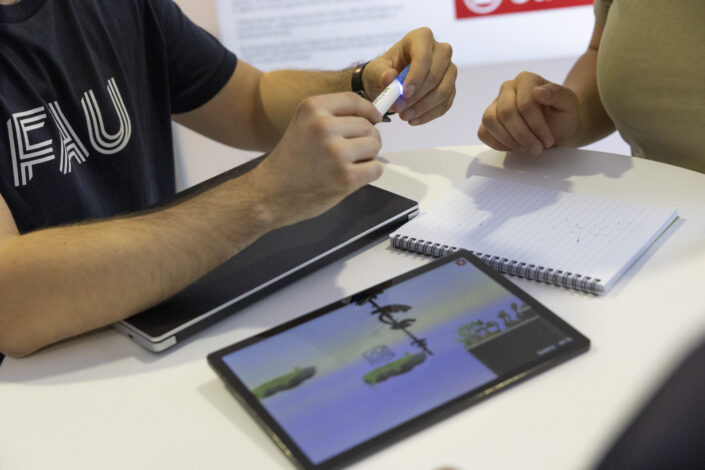
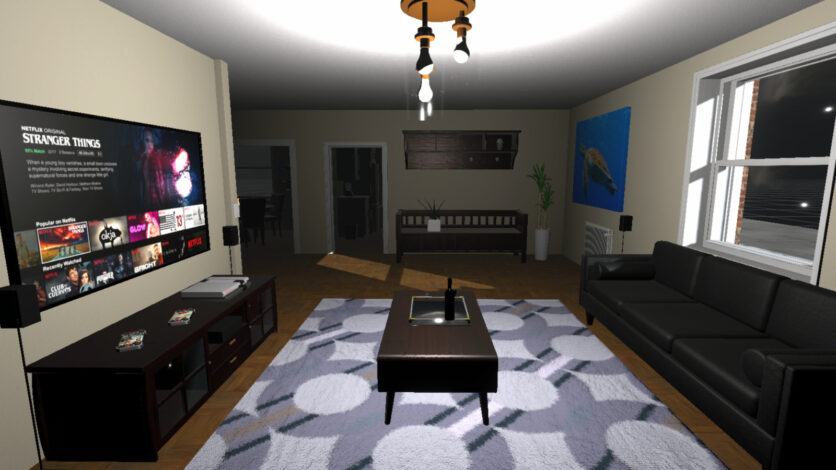
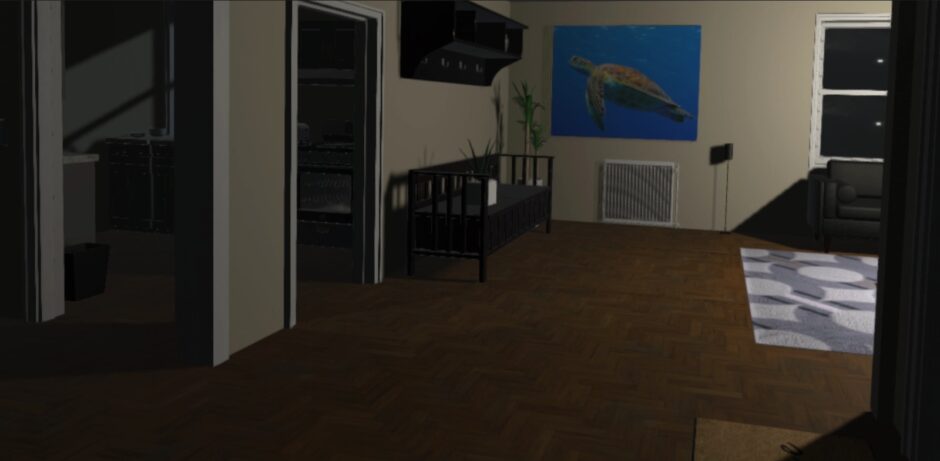
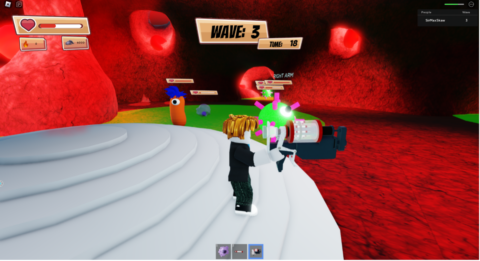
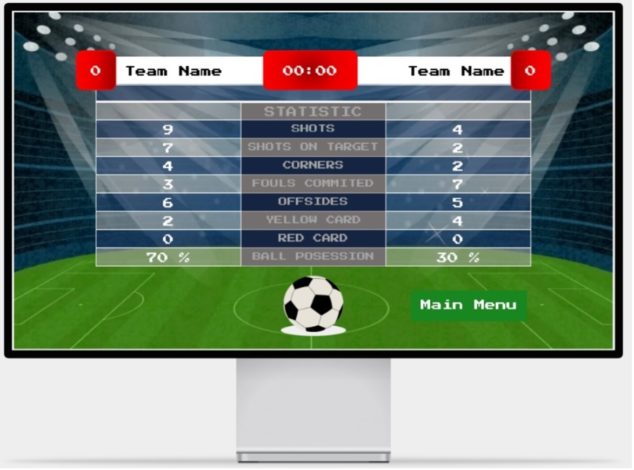
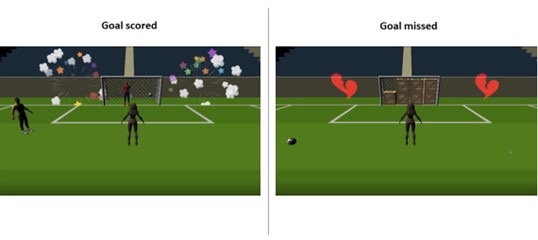
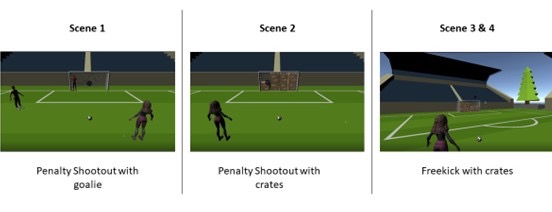
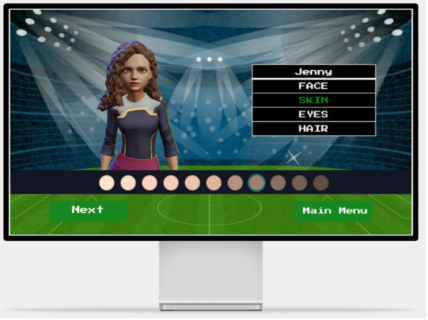
HeartWare is a gamified learning system developed to enhance the educational experience of children by integrating the Stabilo EduPen into a 2D platformer game. The project aims to provide children with fun and interactive breaks during their learning sessions, thereby maintaining high levels of focus and cognitive performance. The game features a robot character, Michael Machini, on a quest to gain empathy by helping animals. Players navigate through levels, collecting gems and transformation triggers, and use the EduPen as the primary input device.
Gamification in educational tools has shown promise in mitigating boredom and lack of concentration in children. The Stabilo EduPen, with its integrated sensors, offers new opportunities for enhancing the learning process. HeartWare aims to leverage these technologies to create an engaging and educational experience that supports children’s learning and motor skill development.
We developed a 2D platformer game using Unity, integrating the Stabilo EduPen as the primary input device. The game comprises a tutorial level and two complete levels, each offering unique challenges and transformations for the player’s character. Our development process included iterative testing and adjustments to enhance gameplay and functionality. Following development, we conducted user testing with adults and children to assess the game’s usability and engagement. Feedback was gathered through guerrilla testing and contextual inquiry methods to understand user experiences thoroughly.
Users responded positively to the game, expressing enjoyment and engagement with the EduPen as an innovative input mechanism. Particularly, children appreciated the game’s challenges and character transformations, highlighting its appeal in educational gaming contexts. However, challenges surfaced during testing, especially among younger children who found controlling the character with the EduPen difficult due to occasional responsiveness issues. Technical feedback indicated instances of slow or unresponsive pen behavior, suggesting areas for improvement in user interface and input responsiveness. Moving forward, we aim to refine the game’s integration with the EduPen, expand the level design with additional challenges and transformations, and align the gameplay experience with Stabilo’s educational objectives.
Items used in this project are licensed based on the Adobe Stock-Medien license.
Global Health – A VR approach for building climate change awareness

Challenge: To foster the understanding of the consequences of one’s actions on climate change, low-threshold accessible and understandable content is needed. Virtual Reality (VR) has emerged as a valuable tool in the field of sustainable development education. However, there remains a lack of practical approaches and empirical insights into fostering climate change awareness through an eco-embodiment perspective. Thus, in our lecture Exergames, we in cooperation with Prof. Dr. Daniel Roth gave our students the challenge:
Develop a virtual reality solution that confronts users in an everyday life simulation with the consequences that may arise if the behavior shown in industrialised countries is calculated on the entire population of Earth.
Date: Winter semester 2022/2023
Lecture: Exergames
Result:
Global Health – a VR approach for building climate change awareness
Team:
Jonathan Denzler, Florian Enders
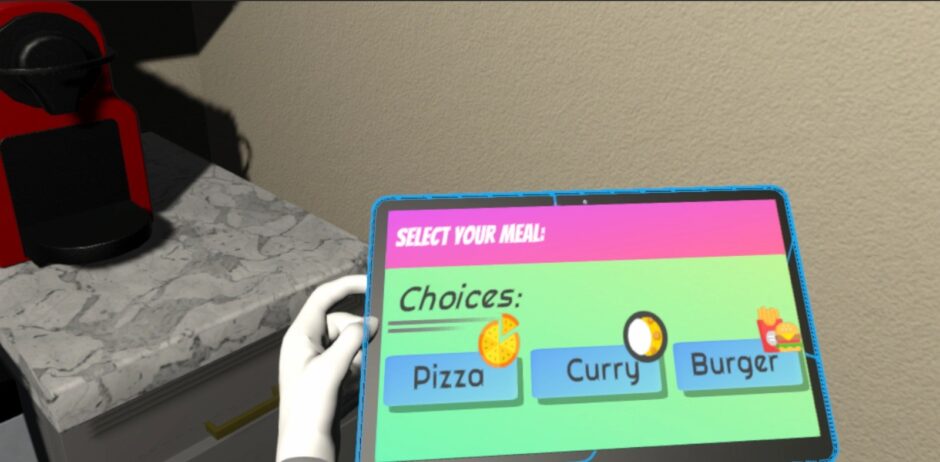
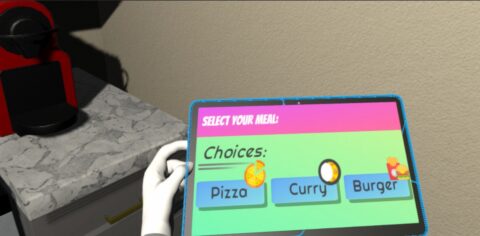
Abstract: “The small things in life” is about showing people the impact of their everyday actions on the climate and thus planet Earth. We created a VR prototype that is set in a virtual apartment where the player has to complete everyday tasks like deciding on which groceries to buy or how to heat their apartment. Emissions of their decisions are tracked in the background and extrapolated over 50 years assuming every person on the planet would live like the player. At the end of the game, the player can see the impact they had on the planet and hopefully gain a new perspective on how their actions influence our climate.
Inflammania 3D – SteamScavengers: Empower macrophages

Challenge:
Game platforms, such as Roblox or Minecraft, are gaining popularity in education as they facilitate the creation of social and immersive learning experiences. However, the potential of this emerging phenomenon for science communication and supporting trust in science has hardly been considered so far. In cooperation with FAU’s Collaborative Research Centre 1181 (CRC1181) we thus develop several connected 3D mini-games that immerse players in the fascinating world of the immune system, increase their understanding of inflammatory mechanisms, and convey knowledge about the latest research of the CRC1181. Accordingly, in summer semester 2023 we gave students of the lecture “Designing Gamified Systems” the following challenge:
Design a strategy game in which the players take over the role of the immune system, make strategic decisions in order to win and learn more about the role of the protein IL-33 and how the immune system is using inflammations to eliminate attackers (for instance, bacteria) and set repair mechanisms in motion.
Reference should be made to current research of the SFB, in particular to the publication “Faas et al., 2021, IL-33-induced metabolic reprogramming controls the differentiation of alternatively activated macrophages and the resolution of inflammation, Immunity 54, 2531-2546. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2021.09.010” .
Lecture: Designing Gamified Systems
Date: Summer semester 2023
Results:
Inflammania 3D – SteamScavengers: Empower macrophages
Team: Maximilian Skawran, Helena Kohl, Laurin Schmid, Yiwei Zheng
Abstract:
This project aims at the development of a video game that conveys biological knowledge in an entertaining and engaging way. It is based on research conducted at the University Clinic in Erlangen, which investigated how macrophages and IL-33 contribute to the resolution of inflammation. We wanted to make these complex biological processes understandable in a way that is accessible to children.
Since children typically do not have extensive knowledge of biology and have limited interest in conventional learning methods, we tackled this challenge with a gamification approach. The mission was to preserve the scientific accuracy of the biological information while creating an engaging game experience. For this reason, this project is based not only on biological research, but also on various gamification theories. In this way, we ensured that the focus is on the fun of the game, while at the same time providing continuous learning outcomes for the players.
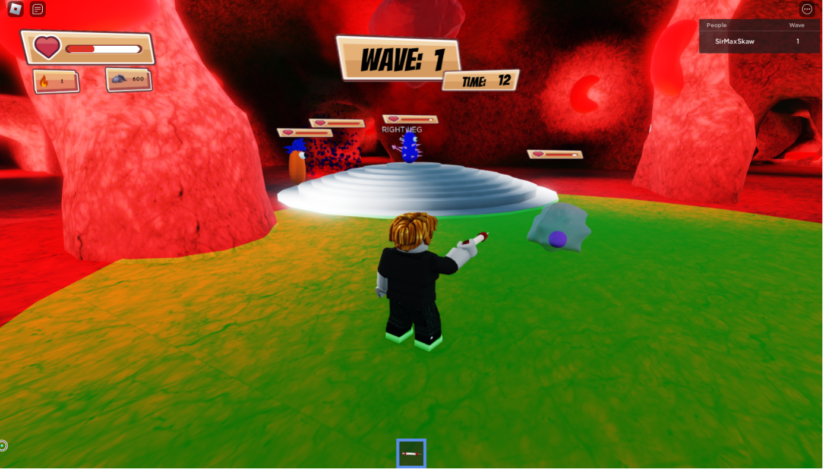
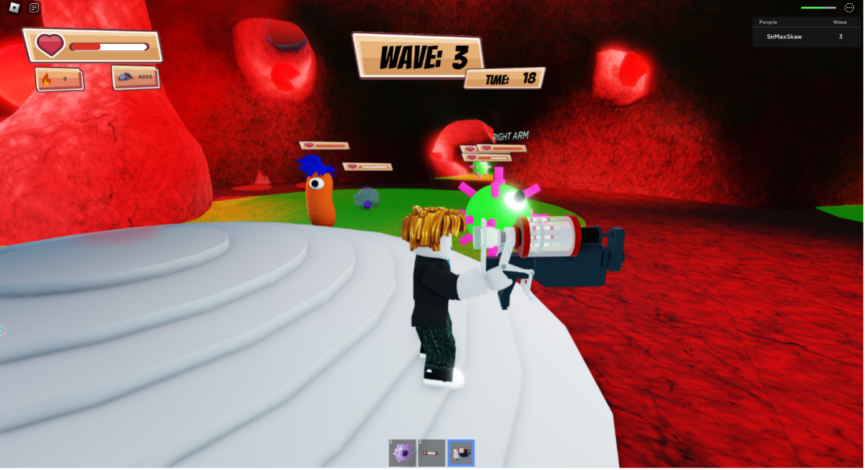
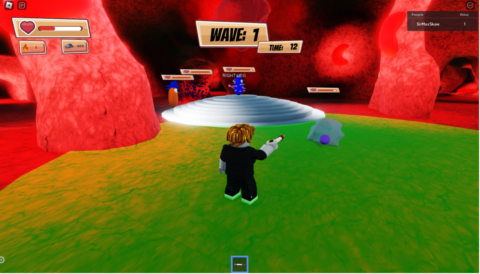
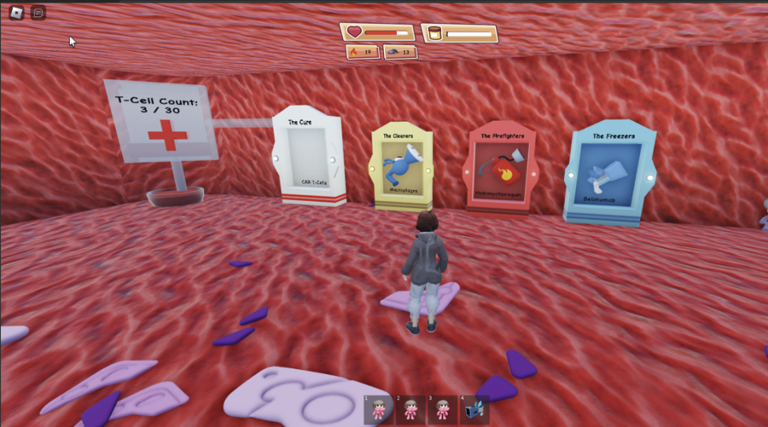
As a result, we developed a game in which players navigate the human body as its immune system. They must protect the heart from various bacteria and viruses by strategically deploying macrophages and using the power of IL-33 to ensure their own survival. To implement this idea, we used Roblox, a popular online platform where users can create, share, and play games designed by others in a virtual environment.
Inflammania 3D – Catch me if you can: The CAR T Cell Solution

Challenge:
The metaverse is becoming increasingly important as it has the potential to revolutionise various industries, including games, entertainment and
commerce, but also to revolutionise education by providing new avenues for collaboration, creativity and economic growth. Accordingly, metaverse platforms such as Roblox offer an unexplored medium for science communication. As part of the CRC1181 research project, several interconnected 3D mini-games will be developed that will form the basis of a virtual, educational world where players will immerse themselves in the fascinating world of the immune system to understand inflammatory mechanisms
and impart knowledge about the latest research. For this, a proof of concept was needed, which was to be created in the seminar “Understanding and Designing the Metaverse” on the basis of the following challenge:
Design a cooperative gameful simulation in Roblox in which the players take over the role of the immune system of a patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) in the novel and revolutionary CAR T-cell therapy developed as part of this FAU research project
Date: Wintersemester 2022/2023
Seminar: Understanding and Designing the Metaverse
Project results:
Inflammania 3D – Catch me if you can: The CAR T Cell Solution
Team: Rebecca Greiner, Simon Merk, Sylvie Reis, Jonathan Stief, Corinna Wüllner
Abstract:
3D metaverse platforms like Roblox have been popularized in various fields as they facilitate the creation of social and immersive experiences. Especially in the context of science communication, however, they still possess a wealth of untapped potential as they could make complex scientific topics more tangible and easier to grasp. Because this potential has so far hardly been explored, we developed a game that transfers knowledge about the autoimmune disease SLE and the newly developed “CAR T-Cell” treatment for it, to examine how it is perceived by users.
“What is SLE?”
It is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect various organs and systems in the body. In systemic lupus erythematosus, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, leading to inflammation and damage. Symptoms of SLE can vary widely from person to person but may include fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes (often in a butterfly pattern across the cheeks and nose), fever, chest pain, hair loss, mouth ulcers, and sensitivity to sunlight. SLE can also affect internal organs such as the kidneys, heart, lungs, and brain, leading to complications in some cases.The novel CAR T-Cell therapy however allows these patients to properly treated for the first time.
During the project a prototype was developed in ROBLOX, that immerses player into the body of a patient, to fight off corrupted B-Cells which reap havoc in the body, causing severe inflammations, that cause the severe impairments for the patients.
For a first evaluation, we conducted user testings in the form of think-aloud protocols and a survey to investigate whether first users enjoy and are immersed into the game and whether they feel they are learning through such an approach. Within the early stage of our research, it has become apparent that games for immersive metaverse platforms have the potential to convey complex scientific knowledge in a fun and understand-able wayand should be investigated further.

Rocket Team

Challenge: Over the past decade, we’ve seen an increasing use of gamification in mobile applications to increase the engagement and fun of athletes in individual training and sports. Gamified applications such as Fitbit, adidas Running, Nike+, Fitocracy, Strava, to name a few, inspire crowds of athletes to exercise regularly. However, there is a lack of knowledge and concepts on how to gamify traditional team sports such as football, basketball, baseball, or floorball and their training. Thus, in cooperation with adidas AG we gave students participating in the lecture Designing Gamified Systems the following challenge:
Design and investigate a novel digital gamification solution for your favorite team sports in order to increase the athlete’s individual or social training experience, their training performance, and the social dynamics (e.g., cohesion and team identity) within a sports team.
Five project teams worked on this challenge and developed impressive concepts and prototypes within two months, which were then presented to adidas AG executives.
Date: Summer semester 2022
Results:
Rocket Team
Team: Dardan Berisha, Florian Enders, Rebecca Greiner, Anna Hollendonner
Abstract:
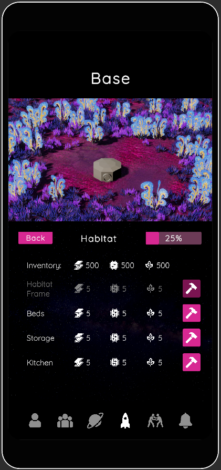
We are Rocket Team. Our vision is to motivate training partners to cooperate easily and thus help them improve upon their individual strengths as well as their team skills. For this purpose, we have developed a gamification approach that engages multiple Volleyball players to cooperatively train together. It is set into a new environment, a foreign planet on which the team must accomplish several challenges to build up a base and a rocket to escape the planet and move on with their mission. This concept is embedded in a mobile application that players can use as part of their training. Within the two-months-project we have developed a minimum viable product in Unity and Blender and investigated on user feedback. In the future, actual training data could be captured with the Adidas GMR tag to measure training success.
- YouTube Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JSnQXlq9wy8

METABALL

Challenge: Over the past decade, we’ve seen an increasing use of gamification in mobile applications to increase the engagement and fun of athletes in individual training and sports. Gamified applications such as Fitbit, adidas Running, Nike+, Fitocracy, Strava, to name a few, inspire crowds of athletes to exercise regularly. However, there is a lack of knowledge and concepts on how to gamify traditional team sports such as football, basketball, baseball, or floorball and their training. Thus, in cooperation with adidas AG we gave students participating in the lecture Designing Gamified Systems the following challenge:
Design and investigate a novel digital gamification solution for your favorite team sports in order to increase the athlete’s individual or social training experience, their training performance, and the social dynamics (e.g., cohesion and team identity) within a sports team.
Five project teams worked on this challenge and developed impressive concepts and prototypes within two months, which were then presented to adidas AG executives.
Date: Summer semester 2022
Results:
Metaball
Team: Jennifer Mitchell, Pavel Akram, Kartik Kanodia, B. S.
Abstract:
Welcome, we are METABALL!
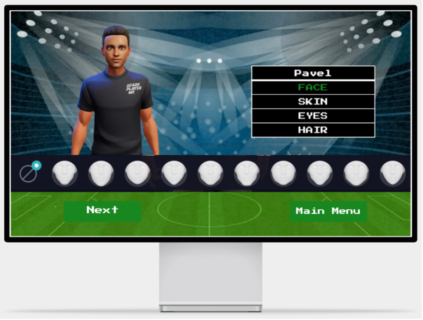
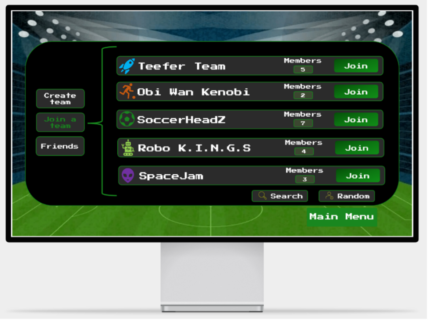
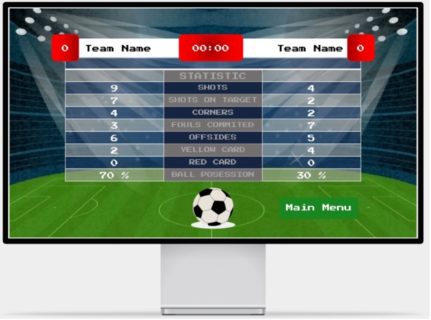
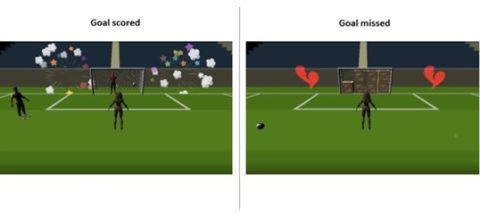
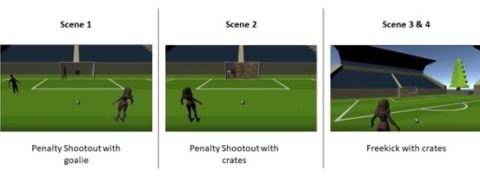
Our team has developed a prototype soccer game in the Metaverse environment using the popular game development engine “Unity 3D”, along with a detailed game menu designed using the web-based design and prototyping tool “Framer”. Our game concept is still in its infancy and a playable one-person 3D game was developed. The overall project revolves around the theme “training meets metaverse”. The goal of our game is to create a gamified mixed reality training system for a team sport. This system should include various virtual components such as virtual goods, virtual worlds, or virtual avatars that ultimately help to strengthen the team identity and cohesion of the players. The game was designed so that players wear a sensor such as the “Adidas GMR” sensor on them during game training in the real world to collect and transfer this data to the virtual world, our game METABALL. This data is used to further develop the system. Our game is unique because the concept of “training meets metaverse” does not yet exist. Our players train and improve their soccer skills individually or in a self-selected team in the real world. In the process, data such as distance, speed, ball hits scored, etc. are recorded and transferred to the virtual game. Depending on how well or badly the player performs in the real world, this also affects his avatar in the game. This is intended to encourage players to develop and improve their skills.
Metactics

Challenge: Over the past decade, we’ve seen an increasing use of gamification in mobile applications to increase the engagement and fun of athletes in individual training and sports. Gamified applications such as Fitbit, adidas Running, Nike+, Fitocracy, Strava, to name a few, inspire crowds of athletes to exercise regularly. However, there is a lack of knowledge and concepts on how to gamify traditional team sports such as football, basketball, baseball, or floorball and their training. Thus, in cooperation with adidas AG we gave students participating in the lecture Designing Gamified Systems the following challenge:
Design and investigate a novel digital gamification solution for your favorite team sports in order to increase the athlete’s individual or social training experience, their training performance, and the social dynamics (e.g., cohesion and team identity) within a sports team.
Five project teams worked on this challenge and developed impressive concepts and prototypes within two months, which were then presented to adidas AG executives.
Date: Summer semester 2022
Results:
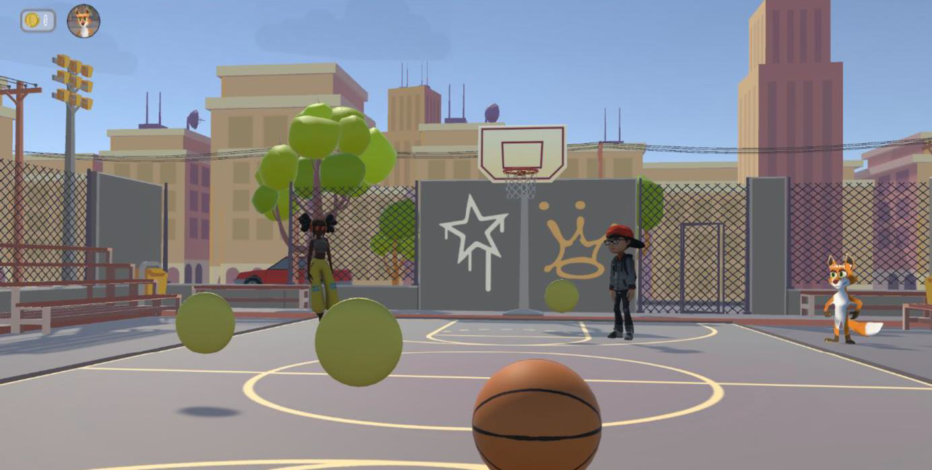
Metactics
Team: Sylvia Reiß, Anna Hirschbeck, Simon Merk, Nico Hambauer
Abstract:
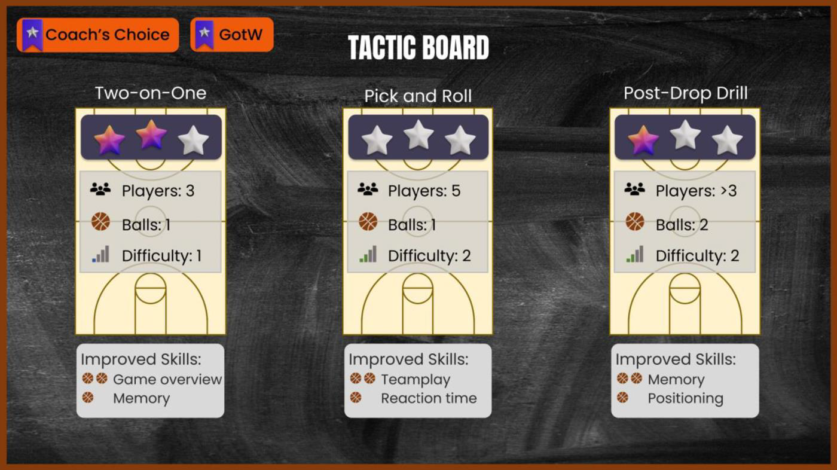
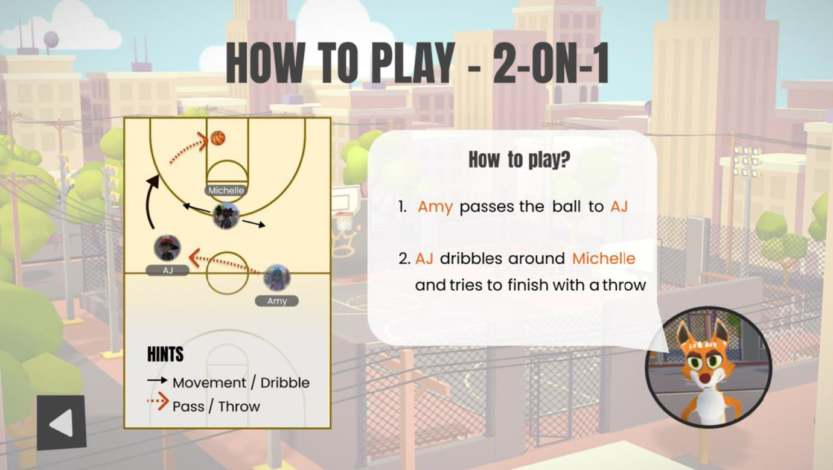
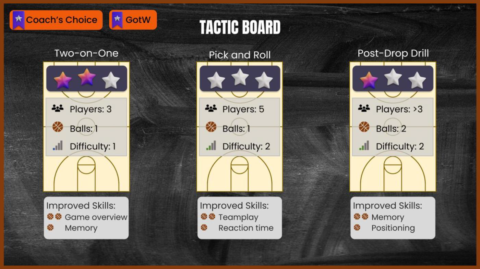
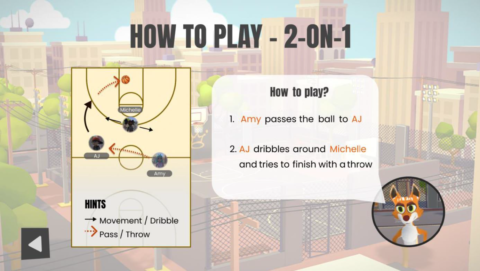
Metactics is a Virtual Reality (VR) approach enabling teams to train their tactical basketball skills anytime from anywhere. Gamers can complete challenges with increasing strategic demands together and learn how to play smart. Thereby, they will be assisted by a virtual team mascot, named Foxy, who will guide them through the game and introduce them to various strategies. In essence, we employ gamification theory to make tactic training in basketball intrinsically more fun and effective. Teams can practice together in the Metaverse, learn new strategic moves and improve their cognitive skills and capability to “think ahead”. Besides the virtual training we provide a social environment in form of a virtual club house. Here teams can hang out enjoy time together and thereby strengthen team cohesion and identity. During the game, players can gain virtual coins, which can be used to acquire virtual goods for their personal avatar or the collective club house.
- YouTube Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Frs0tbX4SDE
- GitLab Repository: https://gitlab.cs.fau.de/ij58osol/gamis-2022
CUBEness

Challenge: In recent years, exploring space has become a trending topic again. Various private organizations such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, or Virgin Galactic and government organizations from the USA, China, India, Europe, or Russia compete for supremacy in space. Besides the exploration of new dimensions, this trend paths the way for innovations that will also change our life on earth. For example, an increasing number of satellites orbiting our earth, offer new possibilities for earth observation and high-speed internet anywhere on earth. This offers new challenges and opportunities, which can be tackled with approaches from game design and gamification. Thus, the task of this semester’s course on Designing Gamified Systems was to:
Design an innovative game or gamification approach in which gaming, space technology and mobility meets in order to either A) improving life on earth or B) improving life in space.
Date: Winter semester 2021
Lecture: Designing Gamified Systems
Result:
CUBEness
Team: Heschu Qarani, Jonathan Stief, Sherwet Galal, Cem Karatasan, Gerrit Sußner
Abstract:
The interest in space is constantly increasing: From space agencies planning longer projects, such as NASAs’ Artemis mission, to private companies such as SpaceX planning to put humans on Mars. Overall, the private sector of space tourism is projected to reach a total of US$1.7 Billion by 2027. The market will expand much further in the future, with long-term missions becoming increasingly frequent.
Yet these long-term missions pose significant strains on both the human body and the mind. First among them is the deterioration of muscles, muscle atrophy, and the cardiovascular system through microgravity. These effects are so severe that even short missions (< 30 days) can cause a muscle volume loss of 5.5 to 15.9 percent. In order to combat these effects, most space agencies employ in-flight exercises of about 2.5 hours six days a week. Secondly, space missions represent the “perfect boring situation” and can invoke mental health issues.
Our VR solution addresses both aspects equally, as it gamifies the required exercise to avoid physical consequences, as well as challenge the players mentally and provides opportunities for experiencing social relatedness. For this, it uses both state-of-the-art VR equipment, as well as a Teslasuit, to not only make the experience feel even more immersive through haptic feedback, as well as the possibility to enhance training effects. The main game consists of resource collection during the exercise and a base-building type game in the phases between workouts. Both take place in VR.
In order to overcome the dullness of the monotonous environment, the game features a story putting the players in a scenario in 2075, where Mars has been colonized, and it is now their shared mission to defend and extend the colony. However, players need to collect resources through exercise to repair and build further modules, which is conducted within the VR game.
In the story mode, they are guided through their exercise by story-related messages, collecting resources while traversing the base and the landscapes of Mars. As voluntariness represents an important point in the acceptance of gamified approaches, however, players also have the option to avoid the story. While exercising, they collect resources by swiping them to the side with their controller. From the collected resources they then have the possibility to build three different types of buildings: (1) shelter domes, which set the defense for the whole colony, (2) windmills, which produce electricity for the colony, (3) greenhouses, which produce oxygen. To increase complexity, create fun, and challenge players mentally, the electricity and oxygen stats must match the shelter, or the colony will be dysfunctional, and the defense will receive a debuff. Players will have to ready their bases for increasingly difficult challenges, such as further alien attacks, sand storms, and similar difficulties that life on Mars would bring. This aims to create a long-time engagement in the player, relying on the immersion and social interaction between the crewmates of the space mission to defend their shared colony.
We use a Teslasuit, a smart textile two-piece full bodysuit, to make the experience immersive and interactive. The suit provides haptic feedback, captures motion and biometric functions. Further, a full-body haptic feedback system is built into the suit with 80 electrostimulation channels, which could be used to provide instant feedback on the players’ performance within the game. It can be functionalized in response to motion capture comparison at any time. No additional equipment will be need. The approach may be used with existing training equipment in space stations such as the ISS.

reHAND

Challenge: The use of digital technologies in rehabilitation processes is constantly increasing. In particular, studies show the advantages of telemedical assistance systems in rehabilitation and aftercare. Such cyber rehabilitation can support patients individually and at home. The aim of the project is to develop an gamified solution for assisting and motivating patients in hand rehabilitation.
Automate rehabilitation procedures with gameful simulations and make it accessible (at home)
Date: Winter semester 2021/2022
Lecture: Exergames
Result:
reHAND − Cyber Rehabilitation for hand injuries
Team: D. Braun, E. Alekseenko, V. Rincon, A. Patoary
Abstract: The human hands have a complex structure. Hand injuries, therefore, have a significant negative impact on multiple life aspects. This project presents a Virtual Reality (VR) Exergame to help medical practitioners receive information on improvement rates and make exercising more attractive to patients. The game has been developed in Unity 3D game engine for the HTC VIVE Focus 3. The reHAND system performs an error calculation of the user’s hand movements and then provides feedback on the accuracy with which a user can perform an exercise. While playing, a user should protect their garden from the angry jealous neighbor, who throws trash in it. Accordingly, the patient performs certain hand movements to break thrown objects. Further, reHAND covers such motivational affordances as points (intrinsic game score), levels, and storytelling.
GitLab Repository: https://gitos.rrze.fau.de/hex-teaching-2021/exergames/exergames-group-3
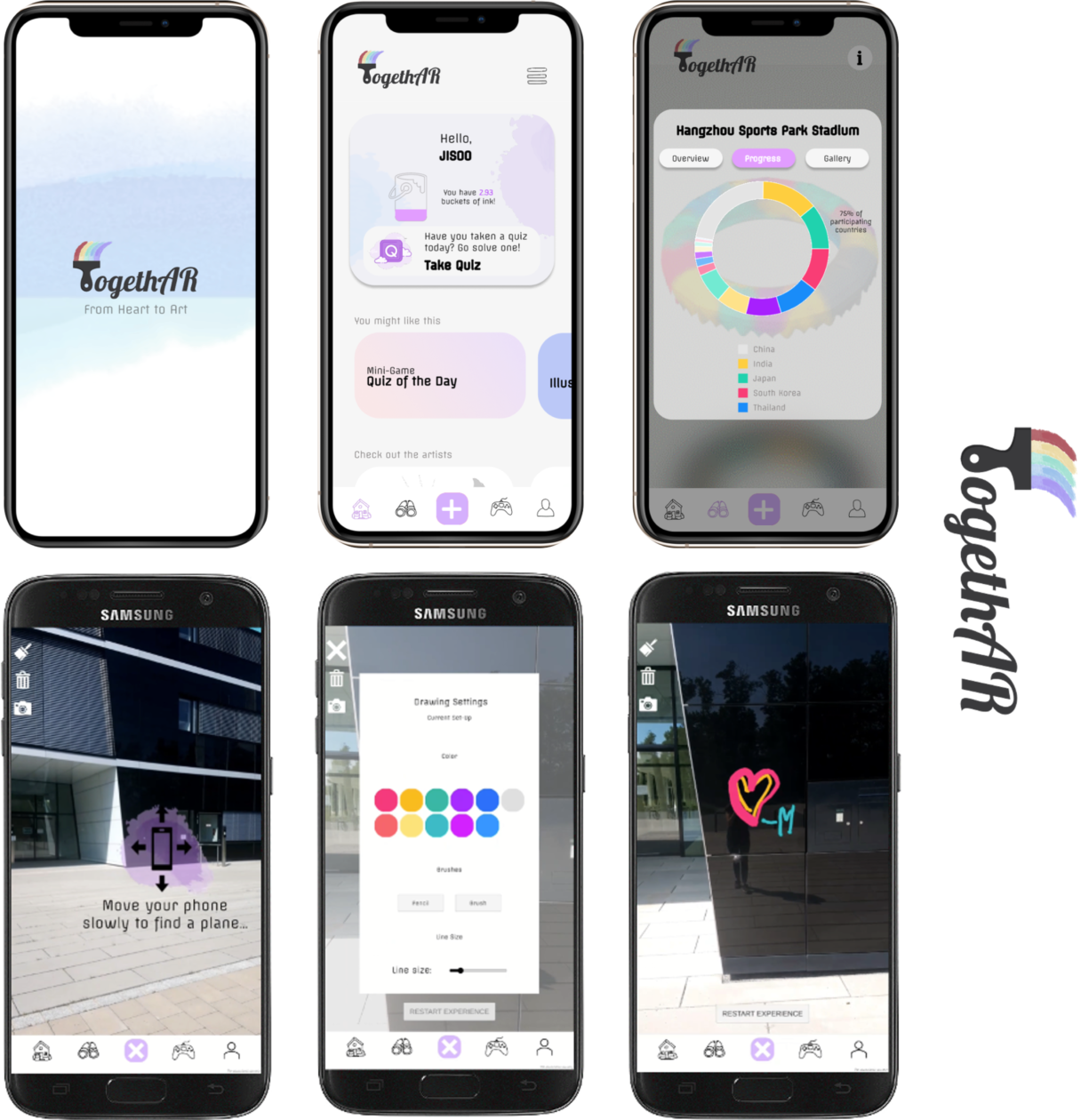
TogethAR
Challenge: Video gaming is on a fast-track to becoming olympic! In 2021 the IOC surprisingly hosted an eSports event as a pre-event of the Olympic Games in Japan and the 19th Asian Games 2022 in Hangzhou will be the first olympic event in which both eSports and sports athletes can receive gold medals in their disciplines. This inspired us. In cooperation with Mercedes-Benz we gave students participating in the lecture Designing Gamified Systems the challenge to:
Design an innovative game or gamification approach in which sports, gaming, and mobility meet as part of an unforgettable mixed-reality experience for potential visitors of the 2022 Olympic Asian Games in China, Hangzhou.
Three project teams worked on this challenge and developed impressive concepts and prototypes within 2 months which were then presented to executives of Mercedes-Benz AG, Daimler AG and MBition GmbH.
Date: Summer semester 2021
Result:
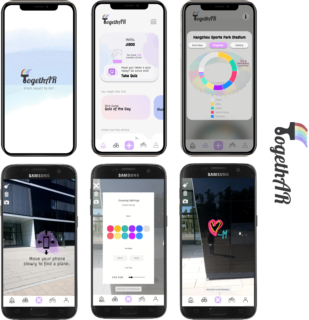
TogethAR − A Gamified App for the Asian Games 2022
Team: K. Horsting, Z. Wen, M. Weber, S. Chen
Abstract: While both the UEFA Euro 2020 and the Olympic Games 2021 in Tokyo occurred under peculiar and extraordinary circumstances due to the current state of the world, the Asian Games 2022 in Hangzhou will hopefully be one of the first big post-pandemic sporting event that allows visitors from all over the world to come together again. To highlight and celebrate the reunion, this gamified approach to a visitor’s guide to the Asian Games engages visitors to contribute to the Olympic spirit by collaborating on a joint artistic symbol of respect, peace, and pluralism in an Augmented Reality (AR) approach while traveling through Hangzhou. The project vision included turning the spectators into active contributors by enabling them to digitally draw on the event venues, which act as canvases for virtual graffiti, sketches, and drawings. Over the course of the Asian Games, the city of Hangzhou would become increasingly colorful, visualizing the collaboration, cooperation, and competition of a diverse userbase that is united in a common goal. The app TogethARrealized this vision by implementing a detailed and comprehensive concept that is based on self-determination theory and the satisfaction of the three basic needs of autonomy, competence, and relatedness. After extensive research on the target audience, representative personas were created whose motivators form the basis for the app’s design. To cater to their wants and needs, the app incorporates a wide variety of game dynamics, mechanics, and components, ranging from social interaction over challenges and competition up to achievements and resources. Up until now, the project stages of preparation, analysis, ideation, and design have been successfully completed. Additionally, a first Minimum Viable Product (MVP) has been implemented and a comprehensive clickable high-fidelity prototype has been created and utilized for early user testing. The next steps of the project therefore consist of further developing, testing, and evaluating the running MVP.